Elena Myasoedova, M.D., Ph.D., is a clinical rheumatologist with specialty interest in inflammatory arthritis. She is an associate professor of medicine and epidemiology and clinical practice, and leads research in rheumatology and specifically inflammatory arthritis at the Mayo Clinic. Dr. Myasoedova’s team submitted a research proposal to access Vivli to conduct analysis relevant to their topic, “Individualized Prediction of Treatment Response to Methotrexate in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Machine Learning Approach”. Their completed research has been presented to the rheumatology research community at conferences and in publications including Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. She sat down with Vivli to tell us more about accessing clinical trial data to advance her research, and the possibilities for using machine learning as a tool in clinical support for people with rheumatoid arthritis.
Please tell us a little bit more about your research – what led you to want to investigate this particular topic?
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, methotrexate is a medicine that is used very commonly, and frequently is the first medicine and the most common medicine used in combination later on during the disease course. The challenge that we are facing in rheumatology in general is that we do not have individualized prediction of response to treatments. This means that we use a trial and error approach to treatments; we start patients on medications that are generally effective and safe, and then if a patient does not respond, we upgrade to a different medicine. Because most of the medicines that we use take weeks and months to show their effects, it’s important to understand early on if a person is likely to be a responder. That would help to save time and potentially save some unwanted side effects for the patient, and also help us to be more proactive and helpful.
For this specific study, we looked at clinical markers or clinical predictors of response to methotrexate. We found more than 1400 patients from 13 randomized trials. A total of 775 patients from 4 RCTs were included in the study, and we monitored their response across a six-month timeframe. We further evaluated whether people who did not respond to methotrexate and had some moderate to high disease activity at 12 weeks – who out of this population would respond by follow-up at 24 weeks. We also found a couple of markers for that: specifically if there was a drop in DAS28 sat rate from baseline to 12 weeks of at least 1 point, then it was predictive of then achieving remission or low disease activity at 24 weeks. Otherwise the chances were slim.
We developed this algorithm, and externally validated it using two independent trials with good results. I think that these findings advance the understanding of who are the most likely responders, and how we should discuss with patients their likelihood of response at the very start of their treatment.
Are you hoping that this is going to change the clinical approach? Has it already had an impact in clinical approaches to working with people who have arthritis?
This particular study, and similar studies would probably change the way we discuss this treatment with a patient; changing the treatment approach is a very complex task that probably has to come through the association guidelines.
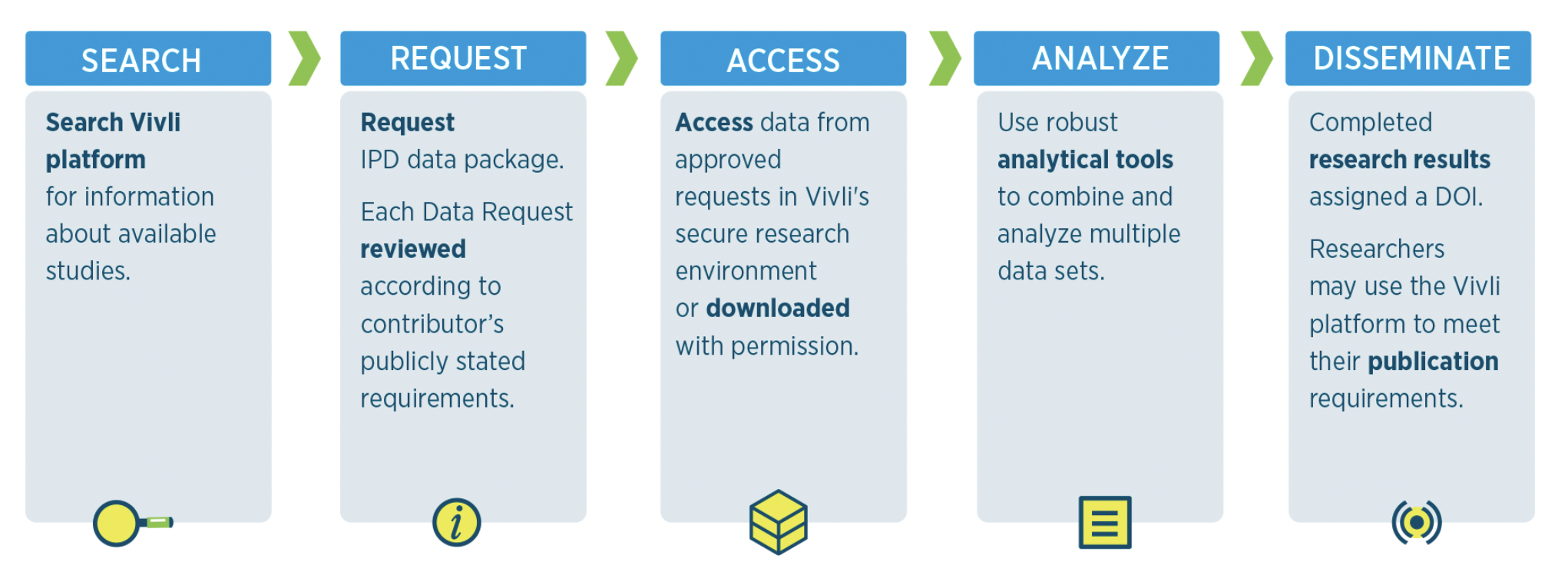
Is there anything specific that you’d like to say about what working with the dataset in Vivli enabled you to do that you might not have been able to do otherwise?
It was actually a very good experience for us to work with Vivli datasets. It provided longitudinal data on patients who were users of methotrexate but not other medicines, and there were hundreds of these patients available from the trials. So it’s a fairly good dataset to work with, and it had multiple data points longitudinally. Also, at each point, there were multiple clinical points collected, so it was fairly comprehensive.
Do you have any advice that you would give to other researchers who might be interested in accessing this type of data using a platform like Vivli?
The most important advice is to put together a comprehensive proposal with a plan right off the bat, to make sure that the timeline is feasible and that the question that they want to address is feasible with the available data – just to make sure that they are not over-expecting or under-planning. I think it’s most important to ensure that the study question matches the data set.
Have you had feedback about your research and findings?
This research has been presented at several conferences, and the comments have mostly been positive, acknowledging the need for developing such algorithms.